BLACKEAGLE
SENIOR MEMBER
How Russia allowed homegrown radicals to go and fight in Syria
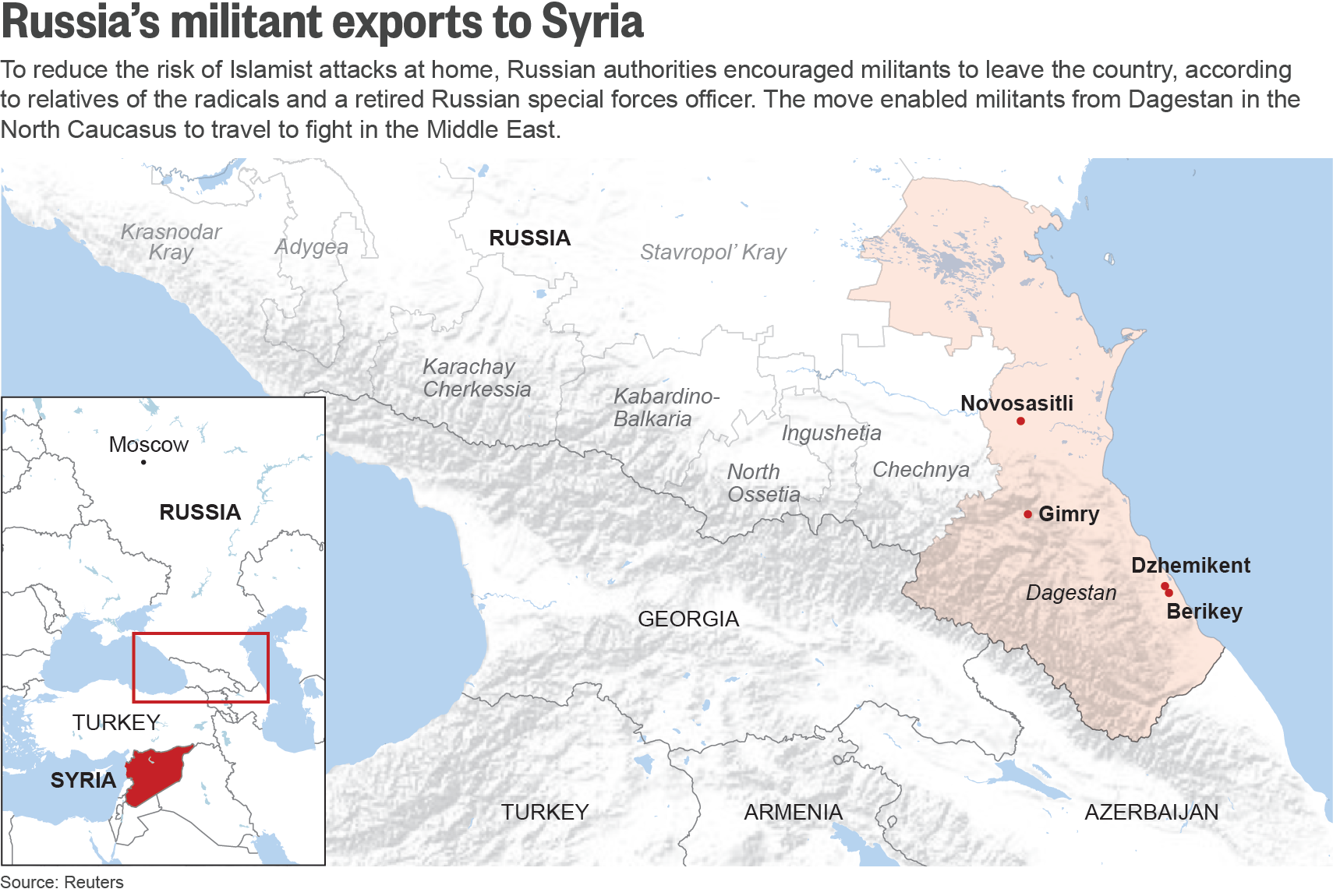
NOVOSASITLI, Russia – Four years ago, Saadu Sharapudinov was a wanted man in Russia. A member of an outlawed Islamist group, he was hiding in the forests of the North Caucasus, dodging patrols by paramilitary police and plotting a holy war against Moscow.
Then his fortunes took a dramatic turn. Sharapudinov, 38, told Reuters that in December 2012 Russian intelligence officers presented him with an unexpected offer. If he agreed to leave Russia, the authorities would not arrest him. In fact, they would facilitate his departure.
“I was in hiding, I was part of an illegal armed group, I was armed,” said Sharapudinov during an interview in a country outside Russia. Yet he says the authorities cut him a deal. “They said: ‘We want you to leave.’”
Sharapudinov agreed to go. A few months later, he was given a new passport in a new name, and a one-way plane ticket to Istanbul. Shortly after arriving in Turkey, he crossed into Syria and joined an Islamist group that would later pledge allegiance to radical Sunni group Islamic State.
Reuters has identified five other Russian radicals who, relatives and local officials say, also left Russia with direct or indirect help from the authorities and ended up in Syria. The departures followed a pattern, said Sharapudinov, relatives of the Islamists and former and acting officials: Moscow wanted to eradicate the risk of domestic terror attacks, so intelligence and police officials turned a blind eye to Islamic militants leaving the country. Some sources say officials even encouraged militants to leave.
The scheme continued until at least 2014, according to acting and former officials as well as relatives of those who left. The cases indicate the scheme ramped up ahead of the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympics because the Russian authorities feared homegrown militants would try to attack the event.
The six Russian militants and radicals identified by Reuters all ended up in Syria, most of them fighting with jihadist groups that Russia now says are its mortal enemies. They were just a fraction of the radicals who left Russia during that period. By December 2015, some 2,900 Russians had left to fight in the Middle East, Alexander Bortnikov, director of the FSB, the Russian security service, said at a sitting of the National Anti-terrorist Committee late last year. According to official data, more than 90 percent of them left Russia after mid-2013.
“Russian is the third language in the Islamic State after Arabic and English. Russia is one of its important suppliers of foreign fighters,” said Ekaterina Sokiryanskaya, a senior analyst for International Crisis Group, an independent body aimed at resolving conflicts.
“Before the Olympics, Russian authorities didn’t prevent departures and a big number of fighters left Russia. There was a very specific short-term task to ensure security of the Olympics … They turned a blind eye on the flow of radical youth” to the Middle East.
Moscow is now fighting Islamic State and other militant groups in Syria that the Kremlin says pose a threat to the security of Russia and the world. The Kremlin has justified its campaign of air strikes in Syria by saying its main objective was to crush Islamic State.

FREE TO GO: Saadu Sharapudinov, a radical from the Russian province of Dagestan, says he was helped by Russian authorities to leave the country. He is pictured here at a location outside Russia in late December 2015. REUTERS/Maria Tsvetkova
But now, according to Sharapudinov, the FSB officer said he was free to leave Russia and that the state would help him go.
"They said: ‘Go wherever you want, you can even go fight in Syria,’" Sharapudinov told Reuters in December. He recalled that the Olympics came up in the negotiations. “They said something like, ‘to let the Olympics pass without incidents.’ They didn’t conceal they were sending out others as well,” he said.
NEW NAME
Sharapudinov had his own reasons for leaving Russia. There were tensions between him and the local emir, who was also the commander of the militant group to which he belonged. When Sharapudinov told his mother of the FSB’s offer, she tearfully asked him to take it, he said, because she did not want him to be a fugitive any longer.
The plan required the involvement of more state machinery: Sharapudinov needed a new passport to leave Russia, according to the former local official who acted as a go-between.
“Since he was on the wanted list, they couldn’t send him out otherwise,” the former official told Reuters.
Sharapudinov said he was handed a new passport when he arrived at the Mineralnye Vody airport in southern Russia in September 2013, where he was escorted by an FSB employee in a silver Lada car with darkened windows. Along with the passport he got a one-way ticket to Turkey.
Sharapudinov showed Reuters the passport that he said had been supplied by the Russian state. It had a slightly different name and date of birth to those recorded for Sharapudinov on an official list of wanted militants. The photograph showed Sharapudinov, who had a beard when he was interviewed for this article, as shaved. He said he had got rid of his beard for the new passport.
While Reuters was unable to confirm the provenance of the passport, neighbours of Sharapudinov and the former official who acted as a go-between confirmed his identity and his story of how he got the document. Sharapudinov asked that the name in the passport, which he uses as his new identity, not be published.
North Caucasus security officials deny that Islamist radicals were intentionally helped out of the country, but agree their absence helped to solve security problems in the region. "Of course, the departure of Dagestani radicals in large numbers made the situation in the republic healthier," said Magomed Abdurashidov from the Anti-terrorist Commission of Makhachkala, the capital of Dagestan.
A security services officer who took part in negotiations with militants from Novosasitli confirmed that a few fighters “laid down arms and came out” from hiding before later travelling to Syria. “Since they disarmed we stopped prosecuting them,” he said.
He said there were cases over a few years but that it had nothing to do with the Sochi Games. He said the security services did not help anyone leave. “If no measures are being taken against them, according to law, they have same rights as every Russian citizen,” he said. “They could get an international passport and leave.”
The security services officer said he did not know Sharapudinov’s case.

FSB FACTOR: Russian President Vladimir Putin with Alexander Bortnikov, right, director of the Federal Security Service (FSB) in 2014. Bortnikov has said that 2,900 Russians have left to fight in the Middle East. REUTERS/Maxim Shemetov
“The departure of Dagestani radicals in large numbers made the situation in the republic healthier.”
Magomed Abdurashidov, Anti-terrorist Commission of Makhachkala
- By Maria Tsvetkova
- Filed May 13, 2016, 1:15 p.m. GMT
NOVOSASITLI, Russia – Four years ago, Saadu Sharapudinov was a wanted man in Russia. A member of an outlawed Islamist group, he was hiding in the forests of the North Caucasus, dodging patrols by paramilitary police and plotting a holy war against Moscow.
Then his fortunes took a dramatic turn. Sharapudinov, 38, told Reuters that in December 2012 Russian intelligence officers presented him with an unexpected offer. If he agreed to leave Russia, the authorities would not arrest him. In fact, they would facilitate his departure.
“I was in hiding, I was part of an illegal armed group, I was armed,” said Sharapudinov during an interview in a country outside Russia. Yet he says the authorities cut him a deal. “They said: ‘We want you to leave.’”
Sharapudinov agreed to go. A few months later, he was given a new passport in a new name, and a one-way plane ticket to Istanbul. Shortly after arriving in Turkey, he crossed into Syria and joined an Islamist group that would later pledge allegiance to radical Sunni group Islamic State.
Reuters has identified five other Russian radicals who, relatives and local officials say, also left Russia with direct or indirect help from the authorities and ended up in Syria. The departures followed a pattern, said Sharapudinov, relatives of the Islamists and former and acting officials: Moscow wanted to eradicate the risk of domestic terror attacks, so intelligence and police officials turned a blind eye to Islamic militants leaving the country. Some sources say officials even encouraged militants to leave.
The scheme continued until at least 2014, according to acting and former officials as well as relatives of those who left. The cases indicate the scheme ramped up ahead of the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympics because the Russian authorities feared homegrown militants would try to attack the event.
The six Russian militants and radicals identified by Reuters all ended up in Syria, most of them fighting with jihadist groups that Russia now says are its mortal enemies. They were just a fraction of the radicals who left Russia during that period. By December 2015, some 2,900 Russians had left to fight in the Middle East, Alexander Bortnikov, director of the FSB, the Russian security service, said at a sitting of the National Anti-terrorist Committee late last year. According to official data, more than 90 percent of them left Russia after mid-2013.
“Russian is the third language in the Islamic State after Arabic and English. Russia is one of its important suppliers of foreign fighters,” said Ekaterina Sokiryanskaya, a senior analyst for International Crisis Group, an independent body aimed at resolving conflicts.
“Before the Olympics, Russian authorities didn’t prevent departures and a big number of fighters left Russia. There was a very specific short-term task to ensure security of the Olympics … They turned a blind eye on the flow of radical youth” to the Middle East.
Moscow is now fighting Islamic State and other militant groups in Syria that the Kremlin says pose a threat to the security of Russia and the world. The Kremlin has justified its campaign of air strikes in Syria by saying its main objective was to crush Islamic State.

FREE TO GO: Saadu Sharapudinov, a radical from the Russian province of Dagestan, says he was helped by Russian authorities to leave the country. He is pictured here at a location outside Russia in late December 2015. REUTERS/Maria Tsvetkova
But now, according to Sharapudinov, the FSB officer said he was free to leave Russia and that the state would help him go.
"They said: ‘Go wherever you want, you can even go fight in Syria,’" Sharapudinov told Reuters in December. He recalled that the Olympics came up in the negotiations. “They said something like, ‘to let the Olympics pass without incidents.’ They didn’t conceal they were sending out others as well,” he said.
NEW NAME
Sharapudinov had his own reasons for leaving Russia. There were tensions between him and the local emir, who was also the commander of the militant group to which he belonged. When Sharapudinov told his mother of the FSB’s offer, she tearfully asked him to take it, he said, because she did not want him to be a fugitive any longer.
The plan required the involvement of more state machinery: Sharapudinov needed a new passport to leave Russia, according to the former local official who acted as a go-between.
“Since he was on the wanted list, they couldn’t send him out otherwise,” the former official told Reuters.
Sharapudinov said he was handed a new passport when he arrived at the Mineralnye Vody airport in southern Russia in September 2013, where he was escorted by an FSB employee in a silver Lada car with darkened windows. Along with the passport he got a one-way ticket to Turkey.
Sharapudinov showed Reuters the passport that he said had been supplied by the Russian state. It had a slightly different name and date of birth to those recorded for Sharapudinov on an official list of wanted militants. The photograph showed Sharapudinov, who had a beard when he was interviewed for this article, as shaved. He said he had got rid of his beard for the new passport.
While Reuters was unable to confirm the provenance of the passport, neighbours of Sharapudinov and the former official who acted as a go-between confirmed his identity and his story of how he got the document. Sharapudinov asked that the name in the passport, which he uses as his new identity, not be published.
North Caucasus security officials deny that Islamist radicals were intentionally helped out of the country, but agree their absence helped to solve security problems in the region. "Of course, the departure of Dagestani radicals in large numbers made the situation in the republic healthier," said Magomed Abdurashidov from the Anti-terrorist Commission of Makhachkala, the capital of Dagestan.
A security services officer who took part in negotiations with militants from Novosasitli confirmed that a few fighters “laid down arms and came out” from hiding before later travelling to Syria. “Since they disarmed we stopped prosecuting them,” he said.
He said there were cases over a few years but that it had nothing to do with the Sochi Games. He said the security services did not help anyone leave. “If no measures are being taken against them, according to law, they have same rights as every Russian citizen,” he said. “They could get an international passport and leave.”
The security services officer said he did not know Sharapudinov’s case.

FSB FACTOR: Russian President Vladimir Putin with Alexander Bortnikov, right, director of the Federal Security Service (FSB) in 2014. Bortnikov has said that 2,900 Russians have left to fight in the Middle East. REUTERS/Maxim Shemetov
“The departure of Dagestani radicals in large numbers made the situation in the republic healthier.”
Magomed Abdurashidov, Anti-terrorist Commission of Makhachkala





