US Navy Strategies, Operations and Policy

This study was conducted to explain the fundamental principles of US Navy policies, strategies, plans and operational capabilities in times of peace, crisis and war .
Definition of Army and Navy by the United States
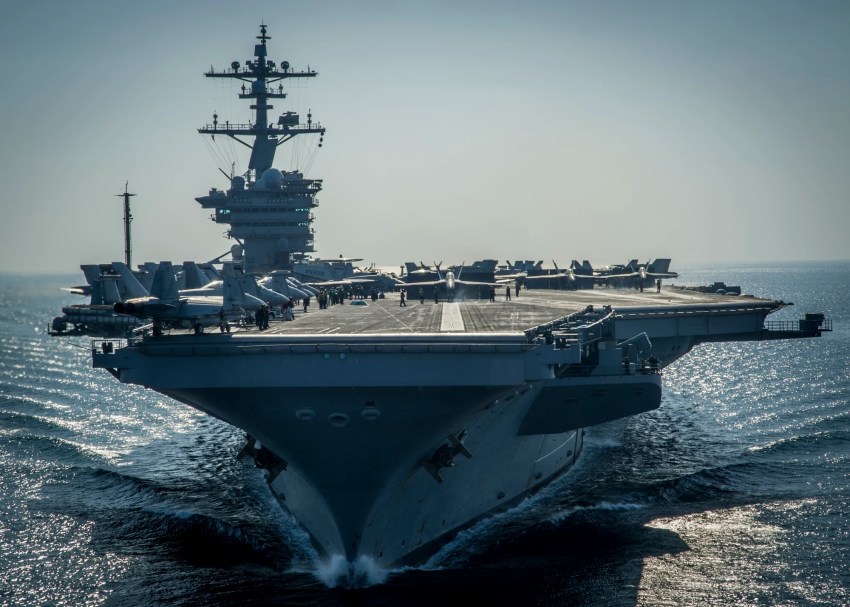

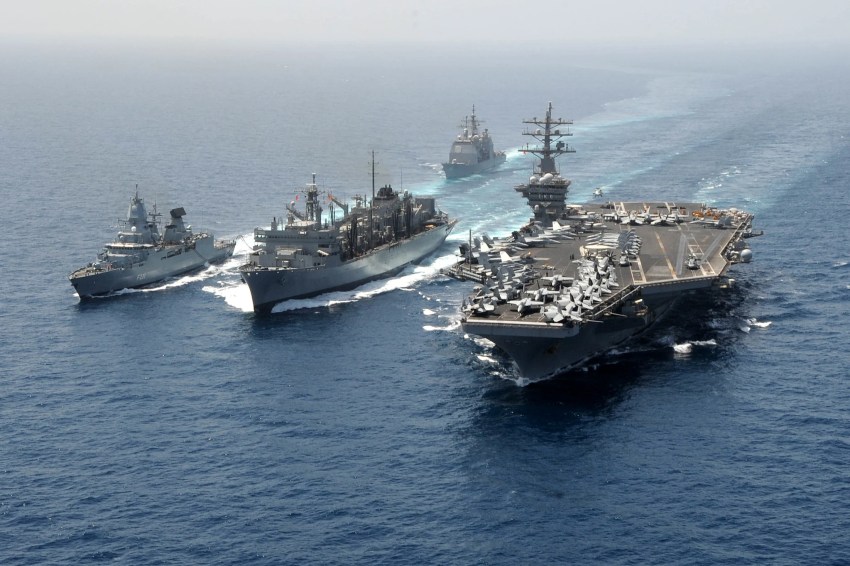
USS Cark Wilson Aircraft Carrier | Basra Bay
1) Peace Time Preparation & Engagement
Objective: It is the priority of the United States navy to protect the security, freedom and welfare of the American homeland, its people and its allies in peacetime.
Roads and Tools: In order to achieve these objectives, the President and the Ministry of Defense are used in various tasks such as deterrence in peace time, assuring allies, preparing for possible wars. In peacetime, the Navy serves the nation and the international community for eight main purposes: strategic nuclear deterrence, ballistic missile defense, conventional crisis and war deterrence, maritime security operations, maritime security operations, humanitarian operations, navy diplomacy, support for science. The capacity of the navy in all these areas allows the President, the Ministry of Defense and the top commanders to carry out national policy.
A) Strategic Nuclear Deterrence
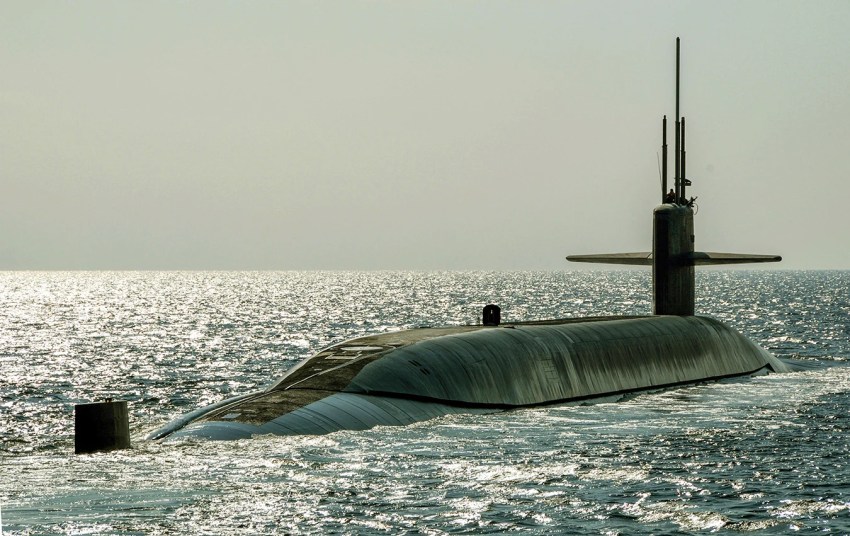

Ohio Class USS Maryland (SSBN 738) Nuclear Attack Submarine | US Navy- Eric Tretter
National strategic nuclear policy and attitude is particularly aimed at deterring possible Russian and/or Chinese strategic nuclear attacks against the United States and its allies/partners. There are two main elements in the United States national strategic nuclear deterrence policy; Ohio-class nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBN) and E-6B are Mercury airborne command aircraft. United States SSBN and SLBM programs take place in close cooperation with the United Kingdom. The UK supports this association with 4 Vanguard Class submarines.
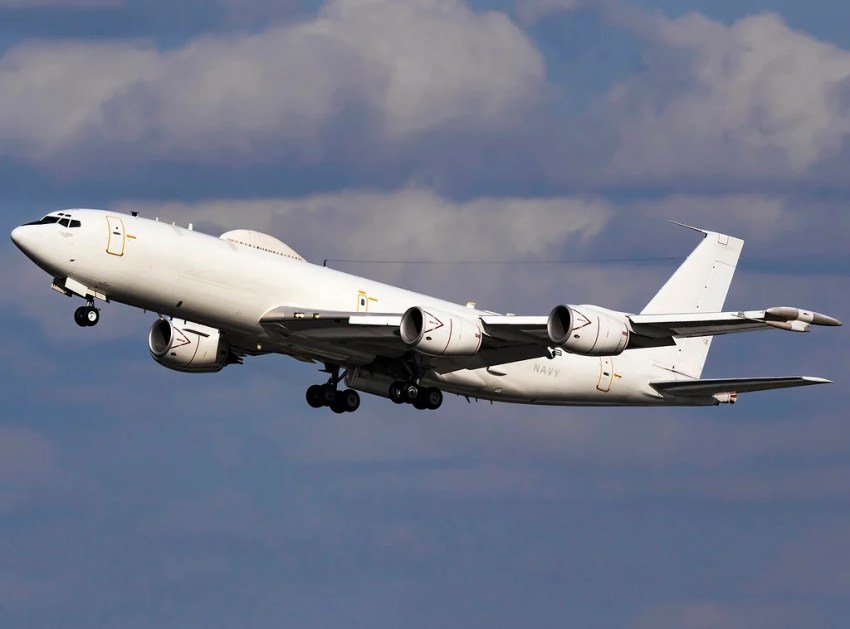

E6B Mercury airborne command control aircraft | Matt Varley [163918]
B) Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD)
The top commanders of the United States routinely deploy cruisers and destroyers (in the North Pacific, the Persian Gulf, the Eastern Mediterranean) capable of ballistic missile defense capabilities connected to the 5th, 6th and 7th fleet and to deploy it to deter possible ballistic missile attacks against the Allies or directly against US elements.

USS Jason Dunham
Several friendly and allied navy - Spain, the United Kingdom, Australia, the Netherlands, Germany, Japan and South Korea - deploy similar marine-deployed anti-ballistic missile (EIC) systems. The United States navy often conducts joint operations with these allies. As part of the EPAA ballistic missile defense, the United States has had a coastal base in Romania since 2014.
C) Prevention of Conventional Crises and Wars
-Preparation
The principal task of the United States navy in peacetime is to prevent possible crises and wars. This role is provided by experienced personnel, material and operational vigilance, forces deployed in the field ready for war and ready to fulfill the directives from the President. Operational elements deal with intelligence, reconnaissance and surveillance (ISR) tasks, as well as exercise and development activities. All these maritime operations are carried out in accordance with long-standing international law.
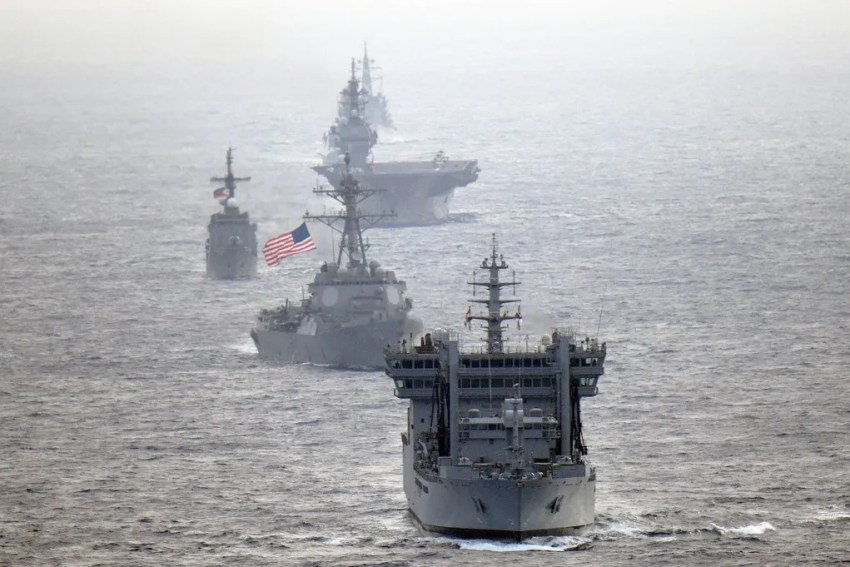

7th Fleet of the US Navy
These methods and objectives contribute to the prevention of crisis and war in peace time with the 5th and 7th fleets in the United States, the Indian Ocean and the Western Pacific. These fleets are the most prepared, balanced and conventional power capacity for war in the United States navy. In the absence of crisis and war missions, these advanced preventive forces help maintain peace and stability in the region. The continuity of the forces in the region is provided in various ways, such as ship and crew rotation.
Aircraft carrier strike force (CSG), ships under ballistic missile defense patrol, amphibious ready groups (ARG), marines expedition groups (MEU) and submarine groups continue to be permanently and readily available in the area with reinforcements from the United States homeland (CONUS). In addition, the American base on the island of Diego Garcia is an important accommodation.
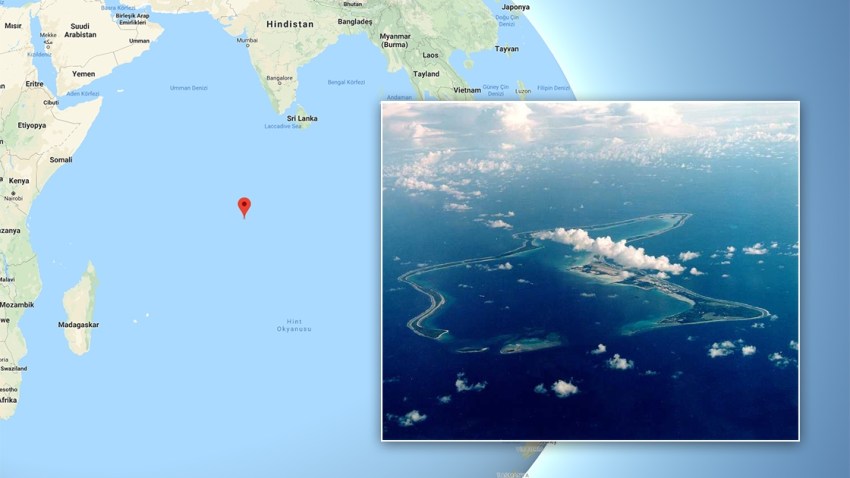 Diego Garcia
Diego Garcia
CSG, ARG / MEU, submarines, mine warfare vessels (affiliated to the 7th fleet) are largely located in advanced bases in Japan and Guam. Coastal combat ships (LCS) are deployed on top of one another in Singapore.
The 6th fleet of the United States is permanently deployed in European and African waters. 6. Fleet also has flagship and maritime patrol aircraft. As mentioned before, in this way the ballistic missile defense capability was obtained in the Eastern Mediterranean. The navy periodically passes from the Mediterranean to the Arabian Sea, and exercises are conducted with the European and North African navy.
- Rebalancing
Since the end of the Cold War, the geographic focus of the US Navy's advanced presence has changed. The North Pacific is still important, even more so, but the American presence in the Arabian and adjacent seas has gained more importance than before. In particular, Operation Enduring Freedom, Operation Iraqi Freedom and Inherent Resolve proved this trend. In addition, the presence of the United States Navy in Atlantic and European waters decreased with the disappearance of the Soviet threat. Even though the modern 6th Fleet was smaller than its presence in the Cold War, its area of responsibility increased, extending beyond the Mediterranean. New Foundland, Bermuda, Iceland, United Kingdom, United States The closure of their bases in Sardinia can be read as an indication of this. The current rebalancing zones are emerging in Southwest Asia in the Western Pacific rather than Atlantic and Western European waters. Although the United States' presence in Europe has remained the same for years, the importance given to the base in Spain is increasing.
- Force Protection
The peacekeeping attitude of the United States Navy for wartime is in the direction of force conservation inside and outside. In 2000, Al Qaeda struck the destroyer USS Cole (DDG-67), which was refueling in Aden Port of Yemen, with a guided missile, revealing the importance of force conservation even in peacetime. The United States navy then changed its rules of engagement (RoE). The Navy has established closer relations with the Criminal Research Service.
-Experience
The ongoing US navy experience is in the form of a fleet, but today requires challenging decisions. The United States navy, alternating between the two options, has to choose whether to maintain deterrence or to wage a war that will occur. For the time being, the Navy is looking forward to presence in the seas and encouraging new developments if successful. The Sea Shadow (IX-529) experimental ghost ship is an important example of this.
ENTRIES financing
Most of the operations are carried out in engagement with other navy and armed forces. The United States navy needs and is operating with a wide range of partners. The navy engagement has proved that navy meets the vital needs of a crisis or war situation, as well as peacetime that ensures international relations and international security. Bilateral and multiple exercises mean the ability to cooperate with allied and/or friendly navies and build professional relationships. The following are the periodic exercises with bilateral and multiple participants:

United States warship joining Foal Eagle
Other obligations include port visits, staff exchange, staff meetings, exercises, and for the purpose of acquisition/research between the United States and its partner/allies. The United States navy routinely hosts staff and volunteer students from allied / partner countries in their schools and exercises. Since 1969, the Navy's Chief Operating Officer (CNO) has been hosting the International Naval Force Symposium (ISS) at Naval War College in Newport. In the period of 2011, naval commander / representatives of 155 countries participated.
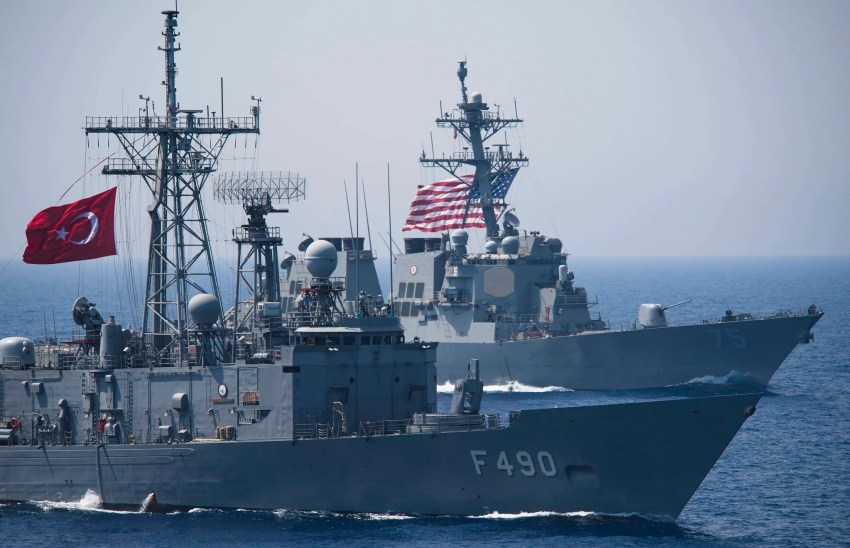

TCG Gaziantep frigate and USS Donald Cook warship joint training
In the case of NATO allies and Korea, the naval structure has been integrated since the Cold War. Common NATO doctrines, tactics / techniques and procedures are implemented extensively and routinely with the participation of several non-NATO navy, helping to promote international joint work.
Long-term NATO institutions enable sustainable and integrated operations and maneuvers of NATO members in the United States, Canada and the European states and in the Balkan / Baltic. The United States considers and encourages multinational activities necessary for future international naval coalitions.
To date, no such large and comprehensive alliance has emerged. The United States is also integrated with other multinational collaborations. The United States navy promotes a tripartite naval approach, in particular the United States / Japan / South Korea. Another example is cooperation between the United States / Japan / Australia navy. In addition, drills are carried out in the Navy of Ukraine and Georgia and the Black Sea.
 BALTIC SEA NATO Drill
BALTIC SEA NATO Drill
Brazil is a traditional navy ally of the United States. The two navy are war allies in both world wars. This alliance continued during the Cold War. The US Navy hopes to continue cooperation as it moves from Brazil to a significantly larger power category.
During the Cold War, the Soviet navy was the greatest potential threat to the United States navy, and the US navy policies, strategies, tactics, and equipment focused mainly on the Soviet navy. Until the Ukraine crisis in 2014, many of the United States' allies and partners were in cooperation with the Russian navy. The Russian Navy participated in the post-Cold War exercises FRUKUS annually with the United States, France and the United Kingdom. It should also be said that participation in BALTOPS exercises and INCSEA summits has been achieved. The Russian Navy was represented at the 2011 International Naval Forces Symposium (ISS) organized by the United States, the 2012 BALTOPS exercise and the 2012 RIMPAC exercises.
Russia and the United States fleets held anti-piracy drills in the Arabian Sea along with many other countries. Prior to 2014, United States navy ships were visiting Vladivostok and other ports.
The United States navy also maintains peace-time cooperation with the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN). As mentioned earlier, the United States navy is no stranger to the Chinese Sea. The United States used its 7th fleet, Tsingtao, from 1945 to 1949 as an advanced operational base. Mutual port visits took place in the 1980s and continued unevenly. PLAN warships acted in conjunction with the navy of the United States and other western states in the Arabian Sea in anti-piracy operations.
In September 2013, the United States Pacific fleet hosted three PLAN warships in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, and held drills in Hawaiian waters. PLAN officers visited the United States in October 2013, and in 2014 the US Navy Chief visited China. In 2014, the PLAN participated in the RIMPAC exercise organized by the United States. Nevertheless, the US navy's convergence with China remains a forced move, as the 1201 section of the US Defense Authorization Act limits military cooperation with China.
Only a handful of countries have not engaged with the United States. North Korea is a prime example. Moreover, there has been no formal engagement with Iran, and the Navy avoids confrontation, especially in the Strait of Hormuz.

This study was conducted to explain the fundamental principles of US Navy policies, strategies, plans and operational capabilities in times of peace, crisis and war .
Definition of Army and Navy by the United States
- The United States is a country of law. The President is the head of the army and navy, so the navy acts in accordance with the President's directives, not independent.
- Since its establishment, the United States has been using the Navy to ensure national security. The Navy has been involved in all wars. The navy is also used as a tool in American diplomacy and economic policy.
- The United States navy rarely acts without allies. During the War of Independence, he used France, the Netherlands and Spain as an advanced base against Britain. During the First World War, Britain and other allies acted together in the North Atlantic and the Mediterranean. In the Second World War, he established the closest relationship with Britain, possibly in alliances known so far (on a Navy basis). During the Cold War, he established close relations with his allies in the Free World.
- Depending on its location, it uses the United States Navy mainly on advanced bases and offshore.
- The US navy review reflects a specific process scope and is divided into three: Peace Time Preparedness & Engagement, Crisis Response, and Combat.

USS Cark Wilson Aircraft Carrier | Basra Bay
1) Peace Time Preparation & Engagement
Objective: It is the priority of the United States navy to protect the security, freedom and welfare of the American homeland, its people and its allies in peacetime.
Roads and Tools: In order to achieve these objectives, the President and the Ministry of Defense are used in various tasks such as deterrence in peace time, assuring allies, preparing for possible wars. In peacetime, the Navy serves the nation and the international community for eight main purposes: strategic nuclear deterrence, ballistic missile defense, conventional crisis and war deterrence, maritime security operations, maritime security operations, humanitarian operations, navy diplomacy, support for science. The capacity of the navy in all these areas allows the President, the Ministry of Defense and the top commanders to carry out national policy.
A) Strategic Nuclear Deterrence

Ohio Class USS Maryland (SSBN 738) Nuclear Attack Submarine | US Navy- Eric Tretter
National strategic nuclear policy and attitude is particularly aimed at deterring possible Russian and/or Chinese strategic nuclear attacks against the United States and its allies/partners. There are two main elements in the United States national strategic nuclear deterrence policy; Ohio-class nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBN) and E-6B are Mercury airborne command aircraft. United States SSBN and SLBM programs take place in close cooperation with the United Kingdom. The UK supports this association with 4 Vanguard Class submarines.

E6B Mercury airborne command control aircraft | Matt Varley [163918]
B) Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD)
The top commanders of the United States routinely deploy cruisers and destroyers (in the North Pacific, the Persian Gulf, the Eastern Mediterranean) capable of ballistic missile defense capabilities connected to the 5th, 6th and 7th fleet and to deploy it to deter possible ballistic missile attacks against the Allies or directly against US elements.

USS Jason Dunham
Several friendly and allied navy - Spain, the United Kingdom, Australia, the Netherlands, Germany, Japan and South Korea - deploy similar marine-deployed anti-ballistic missile (EIC) systems. The United States navy often conducts joint operations with these allies. As part of the EPAA ballistic missile defense, the United States has had a coastal base in Romania since 2014.
C) Prevention of Conventional Crises and Wars
-Preparation
The principal task of the United States navy in peacetime is to prevent possible crises and wars. This role is provided by experienced personnel, material and operational vigilance, forces deployed in the field ready for war and ready to fulfill the directives from the President. Operational elements deal with intelligence, reconnaissance and surveillance (ISR) tasks, as well as exercise and development activities. All these maritime operations are carried out in accordance with long-standing international law.

7th Fleet of the US Navy
These methods and objectives contribute to the prevention of crisis and war in peace time with the 5th and 7th fleets in the United States, the Indian Ocean and the Western Pacific. These fleets are the most prepared, balanced and conventional power capacity for war in the United States navy. In the absence of crisis and war missions, these advanced preventive forces help maintain peace and stability in the region. The continuity of the forces in the region is provided in various ways, such as ship and crew rotation.
Aircraft carrier strike force (CSG), ships under ballistic missile defense patrol, amphibious ready groups (ARG), marines expedition groups (MEU) and submarine groups continue to be permanently and readily available in the area with reinforcements from the United States homeland (CONUS). In addition, the American base on the island of Diego Garcia is an important accommodation.
 Diego Garcia
Diego GarciaCSG, ARG / MEU, submarines, mine warfare vessels (affiliated to the 7th fleet) are largely located in advanced bases in Japan and Guam. Coastal combat ships (LCS) are deployed on top of one another in Singapore.
The 6th fleet of the United States is permanently deployed in European and African waters. 6. Fleet also has flagship and maritime patrol aircraft. As mentioned before, in this way the ballistic missile defense capability was obtained in the Eastern Mediterranean. The navy periodically passes from the Mediterranean to the Arabian Sea, and exercises are conducted with the European and North African navy.
- Rebalancing
Since the end of the Cold War, the geographic focus of the US Navy's advanced presence has changed. The North Pacific is still important, even more so, but the American presence in the Arabian and adjacent seas has gained more importance than before. In particular, Operation Enduring Freedom, Operation Iraqi Freedom and Inherent Resolve proved this trend. In addition, the presence of the United States Navy in Atlantic and European waters decreased with the disappearance of the Soviet threat. Even though the modern 6th Fleet was smaller than its presence in the Cold War, its area of responsibility increased, extending beyond the Mediterranean. New Foundland, Bermuda, Iceland, United Kingdom, United States The closure of their bases in Sardinia can be read as an indication of this. The current rebalancing zones are emerging in Southwest Asia in the Western Pacific rather than Atlantic and Western European waters. Although the United States' presence in Europe has remained the same for years, the importance given to the base in Spain is increasing.
- Force Protection
The peacekeeping attitude of the United States Navy for wartime is in the direction of force conservation inside and outside. In 2000, Al Qaeda struck the destroyer USS Cole (DDG-67), which was refueling in Aden Port of Yemen, with a guided missile, revealing the importance of force conservation even in peacetime. The United States navy then changed its rules of engagement (RoE). The Navy has established closer relations with the Criminal Research Service.
-Experience
The ongoing US navy experience is in the form of a fleet, but today requires challenging decisions. The United States navy, alternating between the two options, has to choose whether to maintain deterrence or to wage a war that will occur. For the time being, the Navy is looking forward to presence in the seas and encouraging new developments if successful. The Sea Shadow (IX-529) experimental ghost ship is an important example of this.
ENTRIES financing
Most of the operations are carried out in engagement with other navy and armed forces. The United States navy needs and is operating with a wide range of partners. The navy engagement has proved that navy meets the vital needs of a crisis or war situation, as well as peacetime that ensures international relations and international security. Bilateral and multiple exercises mean the ability to cooperate with allied and/or friendly navies and build professional relationships. The following are the periodic exercises with bilateral and multiple participants:
- NATO exercises in Europe: Noble Justification, Proud Manta and Brilliant Mariner
- Joint Warrior performed with the United Kingdom
- BALTOPS performed in the Baltic Sea
- Sea Breeze performed by navy in the Black Sea
- Noble Diana performed with Israeli and Greek navy in the Mediterranean
- Phoenix Express performed with North African navy
- Cutlass Express with East African navy
- Obangame Express with West African-European-Brazilian navy
- International Mine Countermeasures Exercise (IMCMEX) in Basra Korfez
- Cooperation Afloat Readiness and Training (CARAT) and Southeast Asia Cooperation Against Terrorism (SEACAT) in Southeast Asia
- Balikatan and PHIBLEX performed in the Philippines
- Malabar performed by the Indian Navy in the Indian Ocean
- Talisman Saber performed in the Southwest Pacific
- Cobra Gold performed with Thailand
- Naval Engagement Activities in Vietnam
- Foal Eagle and Ulchi Freedom performed in Korea
- Keen Edge performed with Japan
- Pacific Bond with Australia and Japan
- Chilemar performed with the Chilean Navy
- PANAMAX, which is implemented to ensure the security of passage in the Panama Canal
- Southern Partnership Station with Latin American and European navy
- Trident Fury performed in Canada and the Pacific
- Rim of Pacific (RIMPAC) performed in Hawaii
- Bold Alligator

United States warship joining Foal Eagle
Other obligations include port visits, staff exchange, staff meetings, exercises, and for the purpose of acquisition/research between the United States and its partner/allies. The United States navy routinely hosts staff and volunteer students from allied / partner countries in their schools and exercises. Since 1969, the Navy's Chief Operating Officer (CNO) has been hosting the International Naval Force Symposium (ISS) at Naval War College in Newport. In the period of 2011, naval commander / representatives of 155 countries participated.

TCG Gaziantep frigate and USS Donald Cook warship joint training
In the case of NATO allies and Korea, the naval structure has been integrated since the Cold War. Common NATO doctrines, tactics / techniques and procedures are implemented extensively and routinely with the participation of several non-NATO navy, helping to promote international joint work.
Long-term NATO institutions enable sustainable and integrated operations and maneuvers of NATO members in the United States, Canada and the European states and in the Balkan / Baltic. The United States considers and encourages multinational activities necessary for future international naval coalitions.
To date, no such large and comprehensive alliance has emerged. The United States is also integrated with other multinational collaborations. The United States navy promotes a tripartite naval approach, in particular the United States / Japan / South Korea. Another example is cooperation between the United States / Japan / Australia navy. In addition, drills are carried out in the Navy of Ukraine and Georgia and the Black Sea.
 BALTIC SEA NATO Drill
BALTIC SEA NATO DrillBrazil is a traditional navy ally of the United States. The two navy are war allies in both world wars. This alliance continued during the Cold War. The US Navy hopes to continue cooperation as it moves from Brazil to a significantly larger power category.
During the Cold War, the Soviet navy was the greatest potential threat to the United States navy, and the US navy policies, strategies, tactics, and equipment focused mainly on the Soviet navy. Until the Ukraine crisis in 2014, many of the United States' allies and partners were in cooperation with the Russian navy. The Russian Navy participated in the post-Cold War exercises FRUKUS annually with the United States, France and the United Kingdom. It should also be said that participation in BALTOPS exercises and INCSEA summits has been achieved. The Russian Navy was represented at the 2011 International Naval Forces Symposium (ISS) organized by the United States, the 2012 BALTOPS exercise and the 2012 RIMPAC exercises.
Russia and the United States fleets held anti-piracy drills in the Arabian Sea along with many other countries. Prior to 2014, United States navy ships were visiting Vladivostok and other ports.
The United States navy also maintains peace-time cooperation with the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN). As mentioned earlier, the United States navy is no stranger to the Chinese Sea. The United States used its 7th fleet, Tsingtao, from 1945 to 1949 as an advanced operational base. Mutual port visits took place in the 1980s and continued unevenly. PLAN warships acted in conjunction with the navy of the United States and other western states in the Arabian Sea in anti-piracy operations.
In September 2013, the United States Pacific fleet hosted three PLAN warships in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, and held drills in Hawaiian waters. PLAN officers visited the United States in October 2013, and in 2014 the US Navy Chief visited China. In 2014, the PLAN participated in the RIMPAC exercise organized by the United States. Nevertheless, the US navy's convergence with China remains a forced move, as the 1201 section of the US Defense Authorization Act limits military cooperation with China.
Only a handful of countries have not engaged with the United States. North Korea is a prime example. Moreover, there has been no formal engagement with Iran, and the Navy avoids confrontation, especially in the Strait of Hormuz.