You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Identify This Weapon
- Thread starter Stealth
- Start date
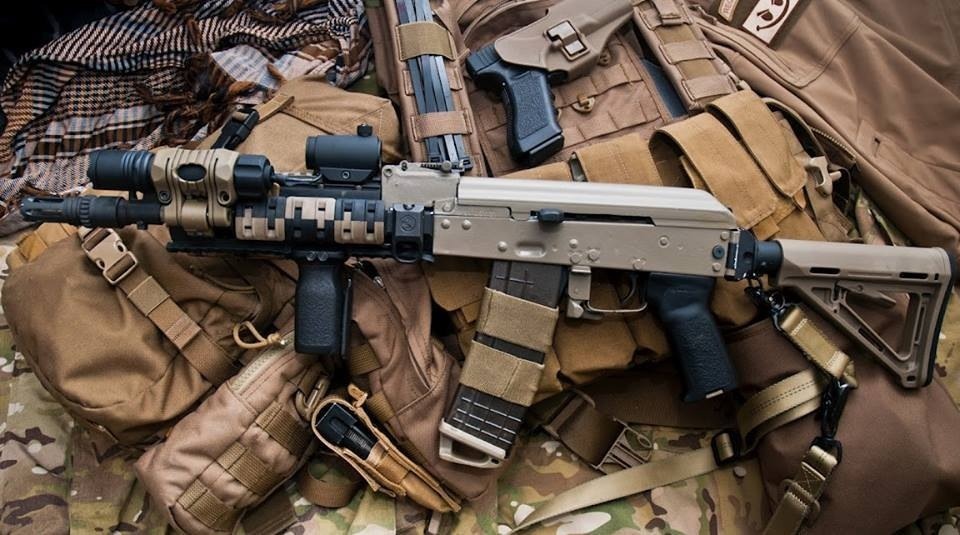
The Kalashnikov AK-12
The Kalashnikov AK-12 (formerly АK-200) is the newest derivative of the Soviet/Russian AK-47 series of assault rifles and was proposed for possible general issue to the Russian Army. In late September 2014, it was announced that it had passed state tests and now is being adopted by Russian Army.


Specifications
Weight 3.3 kg (7.28 lb)
Length 945 mm (37.2 in) (725 mm stock folded)
Barrel length 415 mm (16.3 in); Interchangeable
Cartridge
5.45×39mm
5.56×45mm NATO
7.62×39mm
9×39mm
unknown 6.5 mm
cartridge currently
under development
6.5mm Grendel
7.62×51mm NATO
12 Gauge
Action Gas-operated, long stroke gas piston, rotating bolt
Rate of fire 650 (full auto) or 1000 (3 round burst) rounds/min
Muzzle velocity 900 m/s (2,953 ft/s) with 5.45×39mm
Effective firing range 800 m
Feed system 30-round detachable box magazine, 60-round casket magazine, 95-round drum magazine
Sights Iron; Picatinny rail provided for optics
Variants:
AK-12 - Base Assault Rifle
AK-12U - Carbine Form; shortened barrel and forend.
PPK-12 - Submachine Gun; compact AK-12 version
SVD-12 - Sniper Rifle; dedicated long-range sniper/sharpshooter/designated marksman variant with applicable optics, bipod support and longer barrel assembly.
RPK-12 - Light Machine Gun; 100-round ammunition drum support; heavy duty barrel; optional bipod.

Rainshield7
MEMBER
Out of all the sniper rifles that has been around for years the M82 Barrett was one of those guns that is a videogame and movie featured piece. I could remember playing the game Delta Force that came out in 1998 which had that sniper rifle and it was awesome. I could recall the weapon being in the Rambo movie that came out in 2009. This 50BMG weapon is cool in its overall design and then there is its military counterpart the M107. The M107 is lighter then the M82 I think it had some revamping with the upper receiver but I am not sure. I want to know if anyone else has had any experience with this gun or know about it feel free to share.
Here is a pic of the weapon it is so awesome
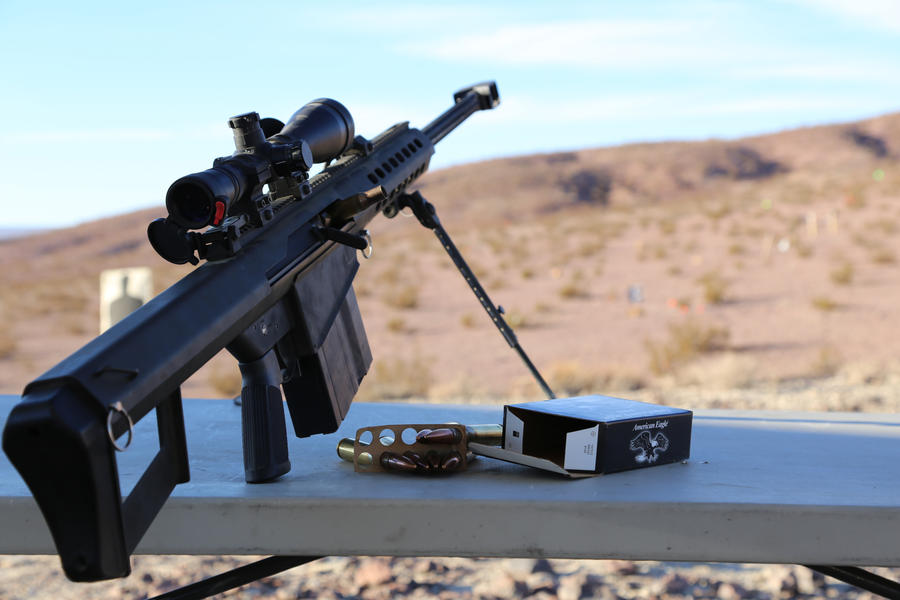

Here is a pic of the weapon it is so awesome

orangesunset
MEMBER
Intersting that Russia is turning away from the Russian equivalent of the 5.56mm round to the 7.62mm round. With the Americans when they moved aways from 7.62 round to the 5.56 round tjere was a great deal of controversy. The 5.56 round has a nasty tendency to tumble after 250 years and it loses its stopping power quickly. The 7.62 round is good for atleast 600 meters.
Can you share with us the specification of this weapon.
Rainshield7
MEMBER
What I know about the weapon is with the original M82 Barrett has been around since 1986 which I believe that the Delta Force had used it on a special operation and had major success. The M82/M107 Barrett sniper rifle is a big sniper rifle with a 10 round magazine. It used to be only chambered for .50BMG but now it also has a bullet called the .416 Barrett. The M82/M107 that is seen now, is called M82A1/M107A1 just to save the confusion. If you are using the M82A1 you can use a conversion kit to convert M82A1 to a .416 Barrett setup. The gun can shoot very far I think up to a few miles and it can take down a helicopter. That is what I kow about the weapon.Can you share with us the specification of this weapon.
Scorpion
THINK TANK: SENIOR
Specifications
Weight
M82A1:
Weight
M82A1:
- 29.7 lb (13.5 kg) (20" barrel)
- 30.9 lb (14.0 kg) (29" barrel)
Length
M82A1:
M82A1:
- 48 in (120 cm) (20" barrel)
- 57 in (140 cm) (29" barrel)
Barrel length
M82A1:
M82A1:
- 20 in (51 cm)
- 29 in (74 cm)
Cartridge
- 50 BMG
- .416 Barrett
Action Recoil-operated, rotating bolt
Muzzle velocity 853 m/s (2,799 ft/s)
Effective firing range 1,800 m (1,969 yd)
Feed system 10-round detachable box magazine
Sights Fixed front, adjustable rear sight; MIL-STD-1913 railprovided for optics
Muzzle velocity 853 m/s (2,799 ft/s)
Effective firing range 1,800 m (1,969 yd)
Feed system 10-round detachable box magazine
Sights Fixed front, adjustable rear sight; MIL-STD-1913 railprovided for optics
Heckler & Koch G36
Created for the requirements of the German armed forces, the G36 continues to set the standard in the field of assault rifles. Used as an infantry weapon in a large number of countries, special forces and security forces also rely on its constant reliability.
Essential components of the G36 are made of glass fibre reinforced plastic. This gives the user a lightweight weapon with high performance and low maintenance requirements.
The G36 is ideally suited for dismounted infantry operations. For optimal handling, weight, and rate of fire in close-quarters battle, and for rapid, accurate and penetrating single fire in long-range combat.
Variants
- G36V (V—Variante "variant"): Previously known as the G36E (E—Export), it is the export version of the standard G36. The G36V has all of the characteristics of the standard rifle with the exception of the sight setup and bayonet mount. It is fitted with a x1.5 or x3 sight and lacks the integrated reflex sight; the bayonet mount is a standard NATO type. This version was produced for Spain and Latvia.
A G36KV configured with a telescopic stock and a Picatinny sight rail- MG36 (MG—Maschinengewehr "machine gun"): Light machine gun version of the G36 equipped with a heavy barrel for increased heat and cook-off resistance.[2] The MG36 and MG36E are no longer offered by H&K.
- G36K (K—kurz "short"): carbine variant with a shorter barrel (fitted with an open-type flash suppressor) and a shorter forend, which includes a bottom rail that can be used to attach tactical accessories, such as a UTL flashlight from the USP pistol. The carbine's barrel lacks the ability to launch rifle grenades and it will not support a bayonet. The weapon retained the ability to be used with the AG36 grenade launcher. G36Ks in service with German special forces are issued with a 100-round C-Mag drum. There are two variants of the G36K. The first and most commonly known has x3 scope/carry handle attached to the top, while the second is the one with the iron sights and rail (no scope included).
- G36KV (formerly G36KE): export version of carbine variant, G36K with sights like G36V.
- G36C (C="Compact", commonly mistaken for "Commando", a term trademarked by Colt Firearms for the CAR-15): This subcarbine model is a further development of the G36K. It has a shorter barrel than the G36K, and a four-prong open-type flash hider or a birdcage type flash hider. The extremely short barrel forced designers to move the gas block closer to the muzzle end and reduce the length of the gas piston operating rod. The handguard and stock were also shortened and the fixed carry handle (with optics) was replaced with a carrying handle with an integrated MIL-STD-1913 Picatinny rail. The dual optical sight found on the standard G36 and G36K models was replaced with a set of rail-mounted detachable iron sights that consist of a semi-shrouded front post and a flip-up rear sight with two apertures of different diameter. The short handguard has four accessory attachment points, one of which could be used for a vertical grip. The G36C was developed and produced in January 2001.

A G36C, equipped with Aimpoint CompM4 red dot sight. It has a shorter barrel than the G36K, and configured with birdcage flash suppressor, a carrying handle with an integrated MIL-STD-1913 Picatinny rail.- G36A2: This is an ordnance designation allocated to an upgraded variant of the G36 used by the German Army. The G36A2 is equipped with a quick-detachable Zeiss RSA reflex red dot sight[22] mounted on a Picatinny rail that replaces the original red dot sight of the dual combat sighting system. The G36A2 upgrade kit also consists of the shorter G36C stock (Designed for better handling with use of body armor and load bearing equipment), new handguard made of aluminium (provides better heat resistance during long periods of firing) with an optional 4 Picatinny rails and a vertical foregrip with an integrated switch for operating an Oerlikon Contraves LLM01 laser light module.
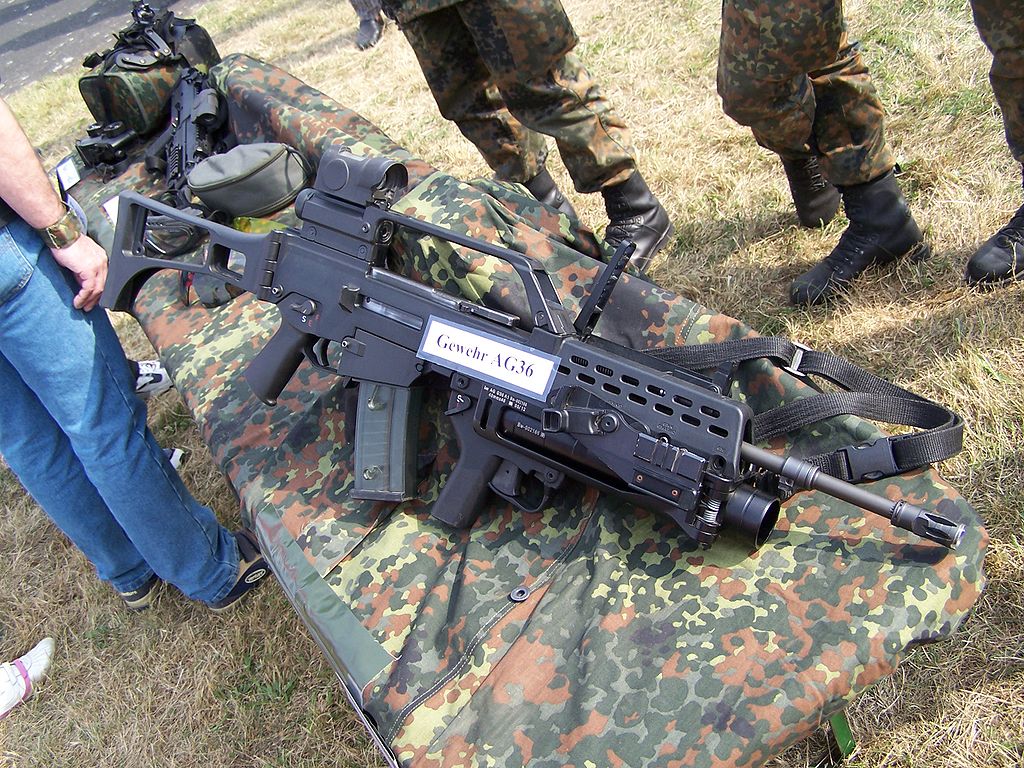

G36A2 with a Zeiss RSA reflex sight and an AG36 grenade launcher on display
G36 | Technical Data
G36 – CAL. 5.56 MM X 45 NATO
- General
- Calibre 5.56 mm x 45
- Operating principle Gas-operated
- Magazine capacity 30 rounds
- Modes of fire SEF
- Rate of fire approx. 750/min
- Sights O, R
- Buttstock FO
- Dimensions
- Length min./max. approx. 755/1002 mm
- Width approx. 65.0 mm
- Height approx. 323.0 mm
- Barrel length approx. 480 mm
- Weight
- Weapon approx. 3,630 g
- Magazine approx. 140 g
- General
- Calibre 5.56 mm x 45
- Operating principle Gas-operated
- Magazine capacity 30 rounds
- Modes of fire 0-1-D
- Rate of fire approx. 750/min
- Sights O
- Buttstock FO
- Dimensions
- Length min./max. approx. 755/1002 mm
- Width approx. 65.0 mm
- Height approx. 277.0 mm
- Barrel length approx. 480 mm
- Weight
- Weapon approx. 3,630 g
- Magazine approx. 140 g

Dual combat sighting system ZF 3x4° as used on German G36A1 assault rifles
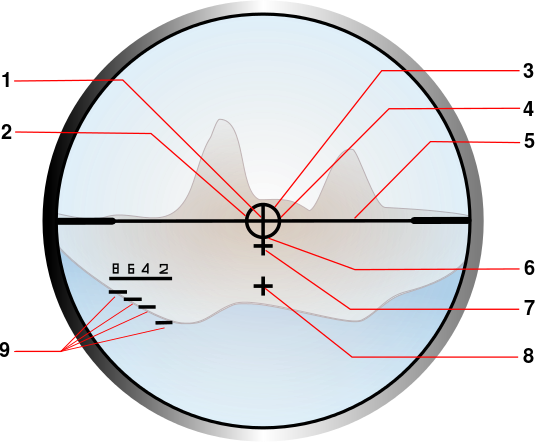
Optical sight reticle pattern
G36 Carbine with two magazines held together jungle style.
Rainshield7
MEMBER
Sweet thanks for sharing the specs on the weapon Scorpion. May I ask where you got the specs from? I knew that the shot pretty far just was trying remember how far.Specifications
Weight
M82A1:
M82A1:
M82A1:
Muzzle velocity 853 m/s (2,799 ft/s)
Effective firing range 1,800 m (1,969 yd)
Feed system 10-round detachable box magazine
Sights Fixed front, adjustable rear sight; MIL-STD-1913 railprovided for optics
revolution
MEMBER
The Steyr AUG is an Austrian bullpup 5.56mm assault rifle, designed in the 1960s by Steyr Mannlicher GmbH & Co KG (formerly Steyr-Daimler-Puch). The AUG (Armee-Universal-Gewehr—"universal army rifle") was adopted by the Austrian Army as the StG 77 (Sturmgewehr 77) in 1978,[3] where it replaced the 7.62mm StG 58 automatic rifle (a licence-built FN FAL).[4] In production since 1978, it is the standard small arm of the Austrian Bundesheer and various national police units.
The rifle and its variants have also been adopted by the armed forces of Argentina, Australia, Bolivia, Ecuador, Ireland, Luxembourg, Malaysia, New Zealand, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia, Pakistan, and the U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement agency.

Specifications
Weight

Steyr AUG A2 (407 mm (16.0 in) barrel) with MIL-STD-1913 rail attached

StG 77
A semi-automatic version of the rifle known as the AUG P is available to the civilian and law enforcement markets. It features a shorter, 407 mm (16.0 in) barrel and a modified bolt, carrier and trigger assembly that will only allow semi-automatic fire. The rifle also has a slightly different optical sight that features a reticule with a fine dot in the centre of the aiming circle, allowing for more precise aiming.
The rifle and its variants have also been adopted by the armed forces of Argentina, Australia, Bolivia, Ecuador, Ireland, Luxembourg, Malaysia, New Zealand, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia, Pakistan, and the U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement agency.

Specifications
Weight
- 3.6 kg (7.9 lb) (Standard)
- 3.3 kg (7.3 lb) (Carbine)
- 3.2 kg (7.1 lb) (Subcarbine)
- 3.9 kg (8.6 lb) (HBAR)
- 3.3 kg (7.3 lb) (Para)[1]
Length
- 790 mm (31.1 in) (Standard)[1]
- 690 mm (27.2 in) (Carbine)
- 630 mm (24.8 in) (Subcarbine)
- 900 mm (35.4 in) (HBAR)
- 665 mm (26.2 in) (Para)[1]
Barrel length
- 508 mm (20.0 in) (Standard)[1]
- 407 mm (16.0 in) (Carbine)
- 350 mm (13.8 in) (Subcarbine)
- 621 mm (24.4 in) (HBAR)
- 420 mm (16.5 in) (Para)[1]
Cartridge
- 5.56×45mm NATO[1]
- 9×19mm Parabellum[1]
Action Gas-operated, Rotating bolt
Rate of fire 680-750 rounds/min[2]
Muzzle velocity Standard rifle: 970 m/s (3,182 ft/s)
Effective firing range 300 metres (980 ft)
Maximum firing range 2,700 metres (8,900 ft)
Feed system
Rate of fire 680-750 rounds/min[2]
Muzzle velocity Standard rifle: 970 m/s (3,182 ft/s)
Effective firing range 300 metres (980 ft)
Maximum firing range 2,700 metres (8,900 ft)
Feed system
- 5.56×45mm NATO: 30 or 42-round box magazine,[1]
- 9×19mm Parabellum: 25 or 32-round MPi 69box magazine[1]
Sights Swarovski 1.5x telescopic sight, emergency battle sights, various optics
Variants

Steyr AUG A2 (407 mm (16.0 in) barrel) with MIL-STD-1913 rail attached

StG 77
A semi-automatic version of the rifle known as the AUG P is available to the civilian and law enforcement markets. It features a shorter, 407 mm (16.0 in) barrel and a modified bolt, carrier and trigger assembly that will only allow semi-automatic fire. The rifle also has a slightly different optical sight that features a reticule with a fine dot in the centre of the aiming circle, allowing for more precise aiming.
Last edited:
revolution
MEMBER
Variants

Steyr AUG A1 (407 mm (16.0 in) barrel)

Steyr AUG A3

Steyr AUG 9 mm

Steyr AUG A1 (407 mm (16.0 in) barrel)
Based on the AUG, Steyr developed the 9 mm AUG submachine gun that fires the 9×19mm Parabellum pistol cartridge. It is an automatic, blowback-operated model that fires from a closed bolt. Unlike the rifle variants, this SMG has a unique 420 mm (16.5 in) barrel with six right-hand grooves at a 250 mm (1:9.8 in) rifling twist rate, ended with a recoil compensator, a slightly different charging handle and a magazine well conversion insert enabling the use of standard 25-round box magazines from the Steyr MPi 81 and TMP submachine guns. A conversion kit used to transform any rifle variant into the submachine gun is also available. It consists of a barrel, bolt, adapter insert and magazine.

Steyr AUG A3
-
- AUG A0: Standard version introduced in 1978.
- AUG A1: Improved version introduced in 1982. Available with a choice of olive or black furniture.[10]
- AUG A2: Similar to the AUG A1, but features a redesigned charging handle and a detachable telescopic sight which can be replaced with a MIL-STD-1913 rail.[10] Introduced in December 1997.
- AUG A3: Similar to the AUG A2, but features a MIL-STD-1913 rail on top of the receiver, and an external bolt release.[11]
- AUG A3 SF (also known as the AUG A2 Commando): Similar to the AUG A2, but features MIL-STD-1913 rails mounted on the telescopic sight and on the right side of the receiver, and includes an external bolt release.[12] It was adopted by the Austrian Special Forces in late 2007.[13] The sight is offered in 1.5x or 3x magnification.
- AUG A3 SA USA: Semi-automatic AUG A3 with a 407 mm (16.0 in) barrel, made available for the U.S. civilian market in April 2009.[14][15]

Steyr AUG 9 mm
- AUG P: Semi-automatic AUG A1 with a shorter, 407 mm (16.0 in) barrel.
- AUG P Special Receiver: Similar to the AUG P, but features a MIL-STD-1913 rail on top of the receiver.
- AUG Para (also known as the AUG SMG or AUG 9mm): Chambered in 9×19mm Parabellum and produced since 1988.[1]Differs from A1 model in barrel, bolt, magazine and a magazine well adapter, which allows the rifle to feed from Steyr MPi 69magazines. This version operates as a blowback firearm, without use of the rifle's gas system.[16] For some time a kit of the above components was available to convert any AUG into a 9 mm variant.[17]
- AUG A3 Para XS: 9mm version of the AUG A3, similar to the AUG Para. Features a 325 mm (12.8 in) barrel and Picatinny rail system.[18]
- AUG M203: An AUG modified for use with the M203 grenade launcher.
- AUG LSW (Light Support Weapon): A family of light support versions of the AUG.
- AUG HBAR (Heavy-Barreled Automatic Rifle): A longer, heavier-barreled version for use as a light machine gun.
- AUG LMG (Light machine gun): Based on the AUG HBAR, fires from an open bolt, has 4x rather than 1.5× optic of the base AUG.
- AUG LMG–T: Same as LMG, but has rail similar to the AUG P Special Receiver.
- AUG HBAR–T: A designated marksman rifle based on the HBAR with a universal scope mount cast into the receiver and fitted with a Kahles ZF69 6×42 optical sight.
- AUG Z: Semi-automatic version, somewhat similar to the A2, intended primarily for civilian use.
- AUG SA: Semi-automatic version of the A1 variant; built for civilian use and import to the US before being banned from importation in 1989.
- USR: An AUG A2 modified to meet the former Federal Assault Weapons Ban (AWB) (or Public Safety and Recreational Firearms Use Protection Act) regulations. The primary difference is the omission of the flash hider.
- AUG A3 SA NATO: Uses a right-hand-only, NATO STANAG magazine stock assembly.[19][20]
- AUG A3 M1: Semi-automatic version, somewhat similar to the A3 SF but with a detachable optical sight which can be replaced with MIL-STD-1913 rails, manufactured in the US by Steyr Arms since October 2014.[21]
Last edited:
revolution
MEMBER
(Users)

 Argentina: Argentine Armed Forces
Argentina: Argentine Armed Forces


-
Australia: Entered service in 1989 as the new issue weapon of the Australian Defence Force. The first regular unit to be issued with the F88 was 6RAR, who received them in January 1989. Rifles are built locally by Thales Australia under licence from Steyr Mannlicher.
-
Austria: Standard service weapon of the Bundesheer, serving as the StG 77 in official army nomenclature.[3] Also used by EKO Cobra.

-
Belgium: In use with the Federal Police.
-
Bolivia.

-
Brazil: In use by Agência Brasileira de Inteligência since November 2011.

-
Bulgaria: SOBT (counter-terrorist unit) only.

-
Cameroon

-
Croatia: Special forces.

-
Djibouti
-
Ecuador

-
Gambia

-
Hong Kong: A1 variant used by Special Duties Unit of the Hong Kong Police Force.[citation needed]
-
Indonesia: Komando Pasukan Katak (Kopaska) tactical diver group and Komando Pasukan Khusus (Kopassus) special forces group. Also used by Brigade Mobil special forces group of the Indonesian National Police, including Detasemen Khusus 88 counter-terrorist unit.[citation needed]

-
Ireland: Standard service rifle of the Irish Defence Forces. Army Ranger Wing special forces use Steyr AUG A2 and A3.
-
Italy: Carabinieri special forces: Gruppo di Intervento Speciale and 1st "Tuscania" Regiment

-
Kazakhstan: Used by SWAT teams.

-
Luxembourg: Standard infantry rifle of the Luxembourg Army. The HBAR version is also employed as the section support weapon. The Unité Spéciale de la Police intervention unit of the Grand Ducal Police employs the AUG A2 variant.

-
Malaysia: Made under license from Steyr by SME Ordnance. Local production of the AUG rifle series started in 1991with a joint production with Steyr that started in 2004. Lawsuits from Steyr emerged when Malaysia decided to withdraw from joint production.
-
Last edited:


